The Science of Anti-Aging: Can We Really Extend Human Lifespan?
Can science slow down aging and extend human lifespan? Discover the latest breakthroughs in anti-aging research, longevity hacks, and what the future holds.
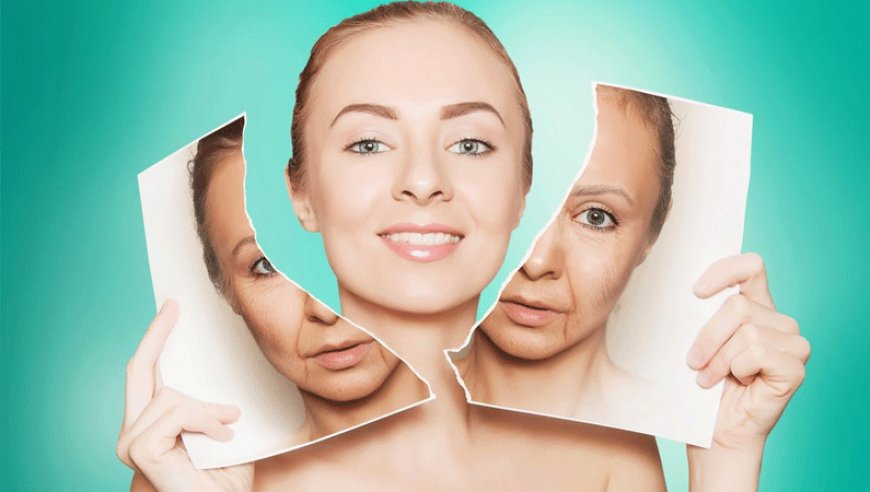

Aging is a natural part of life, but what if we could slow it down—or even reverse it? For centuries, humans have searched for the fountain of youth, from ancient herbal remedies to modern scientific breakthroughs. Today, researchers are uncovering the biological secrets of aging, and some believe we may soon be able to extend human lifespan significantly.
Could we live to 150 or even longer? What are the latest scientific discoveries in anti-aging research? And how can you apply these findings to live a longer, healthier life? Let’s explore the cutting-edge science behind anti-aging and whether it’s truly possible to slow down time.
Why Do We Age? The Biological Clock Inside Us
Aging isn’t just about wrinkles and gray hair—it’s a complex process driven by cellular and molecular changes. Scientists have identified several key reasons why we age:
1. Telomere Shortening
- Telomeres are protective caps at the ends of our chromosomes.
- Each time a cell divides, telomeres get shorter.
- Once they become too short, the cell stops functioning or dies.
2. Cellular Senescence (Zombie Cells)
- Over time, some cells stop dividing but don’t die.
- These "zombie cells" release harmful chemicals that cause inflammation and aging.
3. Mitochondrial Damage
- Mitochondria are the energy powerhouses of cells.
- With age, they become less efficient, leading to fatigue and slower cell repair.
4. DNA Damage
- Everyday stress, UV radiation, and pollution cause DNA mutations.
- The body can repair some damage, but over time, errors accumulate, leading to aging and diseases.
5. Decline in Stem Cells
- Stem cells help repair damaged tissues.
- As we age, the number of functional stem cells decreases, slowing down regeneration.
Understanding these processes is key to finding ways to slow or reverse aging.
Can We Extend Human Lifespan? The Latest Breakthroughs in Anti-Aging Science
Researchers are developing innovative strategies to combat aging, and some studies show we may be able to push human lifespan beyond 100 years. Here’s how:
1. Telomere Extension: Reversing the Clock
Scientists are exploring ways to lengthen telomeres using gene therapy and enzymes like telomerase.
- In a 2015 study, scientists successfully extended the lifespan of mice by increasing telomerase activity.
- Some companies, like BioViva, are testing telomerase-based anti-aging therapies in humans.
2. Senolytics: Killing Zombie Cells
Senolytics are drugs designed to remove aging cells from the body.
- Studies show that clearing these "zombie cells" improves tissue function and reduces age-related diseases.
- Some promising senolytics include quercetin (found in apples) and dasatinib (a cancer drug).
3. NAD+ and NMN Supplements: Boosting Cellular Energy
- NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) is a molecule that declines with age, affecting metabolism and DNA repair.
- Taking NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) supplements has been shown to restore NAD+ levels, improving energy and longevity in mice.
- Harvard scientist Dr. David Sinclair believes NAD+ boosting could slow down human aging.
4. Caloric Restriction and Fasting
- Reducing calorie intake by 20-30% has been shown to extend lifespan in animals.
- Intermittent fasting and time-restricted eating can activate longevity genes, improve metabolism, and reduce inflammation.
5. Longevity Genes and CRISPR Gene Editing
- Some people have naturally occurring longevity genes, like FOXO3, which helps prevent aging-related diseases.
- CRISPR gene-editing technology could allow scientists to modify genes that control lifespan, potentially extending human life by decades.
6. Young Blood Therapy (Parabiosis)
- Studies show that transfusing young blood into older animals can rejuvenate tissues and improve brain function.
- Some Silicon Valley companies, like Altos Labs, are researching ways to use plasma transfusions for anti-aging.
These breakthroughs suggest that scientifically extending lifespan is becoming a real possibility.
Can We Live to 150? The Debate on Human Lifespan Limits
Some scientists believe that the first person to live to 150 is already alive today. However, others argue that there is a natural biological limit to human life.
- The oldest recorded person, Jeanne Calment, lived to 122 years.
- Some studies suggest the human lifespan limit is around 120-130 years due to biological constraints.
- However, advanced therapies like AI-driven medicine, gene editing, and organ regeneration may break past these limits.
How You Can Slow Aging Naturally
Even if radical anti-aging therapies aren’t available yet, you can boost your longevity today by following these science-backed lifestyle habits:
1. Eat an Anti-Aging Diet
- Focus on whole foods, vegetables, and healthy fats.
- Eat foods rich in resveratrol (found in grapes, red wine), curcumin (turmeric), and omega-3s (fish, nuts).
- Reduce processed foods and sugar to prevent cellular damage.
2. Exercise Regularly
- Strength training and aerobic exercise improve heart health, muscle function, and longevity.
- Even walking 30 minutes a day can reduce aging-related decline.
3. Try Intermittent Fasting
- Fasting triggers autophagy, a process that removes damaged cells and regenerates new ones.
- Studies suggest fasting can extend lifespan in animals by 30-40%.
4. Improve Sleep and Reduce Stress
- Poor sleep accelerates aging by increasing inflammation and brain fog.
- Meditation, deep breathing, and relaxation techniques reduce cortisol (the stress hormone), which can slow aging.
5. Stay Socially and Mentally Active
- Engaging in social interactions, learning new skills, and challenging your brain can prevent cognitive decline.
- Studies show that people with strong social connections live longer.
The Future of Anti-Aging: Are We Ready for a Longer Life?
The science of aging is advancing faster than ever. While true immortality may still be far away, breakthroughs in gene therapy, senolytics, and cellular rejuvenation could allow humans to live healthier, longer lives—perhaps to 150 or beyond.
But as science progresses, we must also consider the ethical and social challenges of longer lifespans:
- Will anti-aging treatments be available to everyone or only the wealthy?
- How will society handle overpopulation and resource allocation?
- What will retirement and work look like in a world where people live much longer?
These questions highlight the complexity of human longevity, but one thing is clear: The future of aging is changing, and we may be on the brink of a longevity revolution.
What Do You Think?
Would you take an anti-aging pill if it could extend your life? What’s your ideal lifespan? Share your thoughts in the comments!
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0