The Great Attractor: The Mysterious Force Pulling Galaxies Across the Universe
Discover the Great Attractor, a mysterious force pulling thousands of galaxies—including the Milky Way—toward it. Learn what it is and why scientists are baffled.

Introduction: The Cosmic Enigma That Baffles Scientists
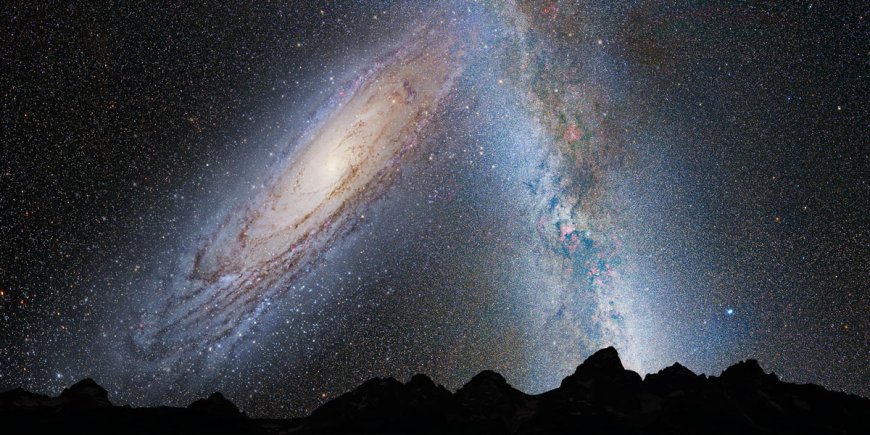
Deep within the vast expanse of our universe lies an invisible, powerful force known as the Great Attractor. This cosmic anomaly exerts an immense gravitational pull on thousands of galaxies, including our own Milky Way. Yet, despite its influence, it remains largely unseen, cloaked by the dense region of the sky called the Zone of Avoidance. Scientists have spent decades trying to unravel the mystery of what the Great Attractor is and why it is drawing an entire region of the universe toward it.
Could this be an enormous supercluster of galaxies? A dense region of dark matter? Or something even more mind-bending? Let’s explore this astronomical puzzle and the groundbreaking research behind it.
What Is the Great Attractor?
The Great Attractor is a gravitational anomaly located approximately 150-250 million light-years away in the Laniakea Supercluster, the vast galactic structure that contains our own Milky Way. It was first detected in the late 1970s and 1980s when astronomers noticed an unexplained motion in our galaxy and its neighboring galaxies.
This motion is known as the "peculiar velocity", a deviation from the expected expansion of the universe. Instead of moving uniformly with the expansion, our galaxy and many others in our cosmic neighborhood are being drawn toward a specific region in space at a speed of about 600 km per second (1.3 million miles per hour)!
But what makes this force so powerful? To understand that, we need to dive into the world of galactic superclusters.
The Role of Superclusters: Mapping the Cosmic Web
Galaxies in the universe are not randomly scattered but arranged in a vast network of structures called the cosmic web. This web consists of galaxy clusters and superclusters, connected by massive filaments of gas, dust, and dark matter.
The Great Attractor sits within one of these vast superclusters, known as Laniakea, which spans over 500 million light-years and contains roughly 100,000 galaxies! This makes it one of the largest known structures in the universe.
However, the exact nature of the Great Attractor remains uncertain. Unlike a black hole, it doesn’t seem to have a singular point of extreme gravity. Instead, it appears to be a region with an unusually high concentration of galaxies, dark matter, and hot gas—all contributing to its powerful gravitational pull.
The Zone of Avoidance: Why We Can’t See It
One of the biggest challenges in studying the Great Attractor is its location behind the Zone of Avoidance, a part of the sky that is heavily obscured by the dust and stars of the Milky Way.
Because of this, visible light telescopes cannot directly observe the region. However, scientists have used alternative methods such as:
- Radio waves – Penetrate dust clouds, allowing astronomers to detect hidden galaxies.
- X-ray observations – Reveal the presence of hot gas and galaxy clusters.
- Infrared surveys – Help identify stars and galaxies blocked by dust in visible light.
Thanks to these tools, astronomers have discovered that the Great Attractor is not a single object but rather part of a much larger gravitational structure!
The Great Attractor vs. The Shapley Supercluster: A Bigger Force at Play?
Recent studies suggest that the Great Attractor may not be the final destination of our galaxy’s motion. Instead, it could be a stepping stone leading us toward an even larger mass concentration: the Shapley Supercluster, located about 650 million light-years away.
The Shapley Supercluster is the most massive galaxy cluster in the observable universe, containing over 8,000 galaxies. Its gravitational pull might be even greater than that of the Great Attractor, meaning our motion could be influenced by a chain of cosmic forces rather than a single point.
This finding changes our understanding of cosmic flows, suggesting that galaxies are constantly moving along gravitational pathways in the universe, much like rivers flowing toward an ocean.
Dark Matter and the Great Attractor: The Invisible Hand?
One of the biggest unsolved mysteries surrounding the Great Attractor is whether dark matter plays a role in its pull.
Dark matter makes up around 27% of the universe’s total mass-energy, yet it remains invisible because it does not emit, absorb, or reflect light. However, it interacts gravitationally with normal matter, meaning it could be a key component of the Great Attractor’s mass concentration.
If dark matter is densely packed in this region, it could be amplifying the gravitational force that is pulling galaxies toward it. Future research and observations may help confirm this theory, shedding light on one of the biggest puzzles in astrophysics.
Will the Milky Way Be Consumed by the Great Attractor?
A common question that arises is whether our galaxy will eventually collide with or be absorbed by the Great Attractor. While we are moving toward it at an incredible speed, the universe’s expansion is also accelerating due to dark energy.
This means that while local motions are dominated by gravity, the overall expansion of the universe may prevent our galaxy from ever reaching the Great Attractor or the Shapley Supercluster. Instead, we are likely to continue moving in that direction while also being influenced by other cosmic forces.
The Future of Great Attractor Research
With advancements in astronomy, we are getting closer to unlocking the mysteries of the Great Attractor. Some of the most promising future research includes:
- The Square Kilometer Array (SKA) – A next-generation radio telescope that will provide unprecedented detail of the hidden universe.
- James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) – Already revolutionizing infrared astronomy, it may help detect new clues about hidden galactic structures.
- Dark Matter Mapping – Using gravitational lensing and other techniques to better understand the role of invisible matter in cosmic flows.
As technology progresses, we may finally uncover the true nature of the Great Attractor and its role in shaping the universe.
Conclusion: A Cosmic Mystery That Continues to Fascinate
The Great Attractor remains one of the most intriguing and perplexing discoveries in modern astrophysics. It challenges our understanding of gravity, galactic motion, and the unseen forces shaping the universe.
Whether it is a collection of galaxy clusters, an unseen mass of dark matter, or part of a much larger cosmic migration, one thing is clear: our universe is far more interconnected than we ever imagined.
As we continue to explore the cosmos, the Great Attractor serves as a reminder of how much we have yet to discover. What other hidden forces are at play in the universe? Only time—and deeper exploration—will tell.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0