Permaculture Living: How to Grow Your Own Food for a Self-Sustaining Lifestyle
Discover how permaculture living can help you grow your own food and create a self-sustaining lifestyle. Learn practical steps to start a thriving, eco-friendly garden.
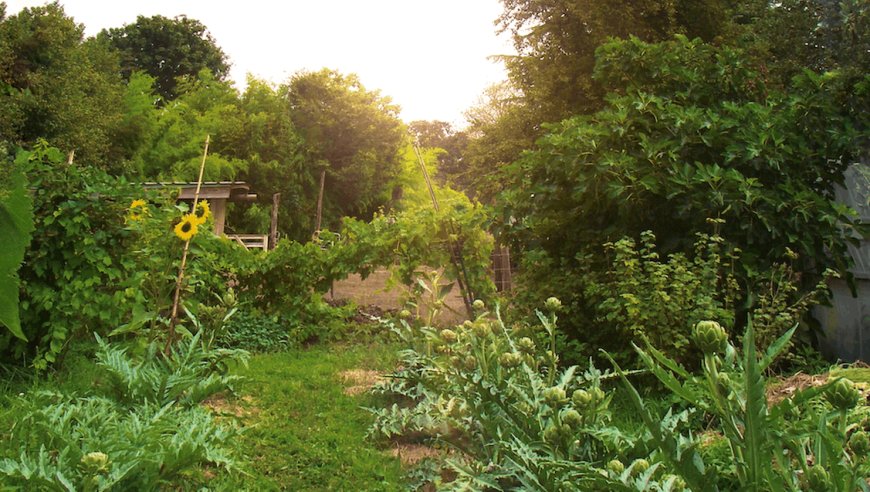

Introduction: The Rise of Sustainable Living
With food prices soaring and environmental concerns growing, more people are turning to permaculture living—a sustainable way to grow food while working in harmony with nature. Unlike traditional gardening, permaculture goes beyond simply planting vegetables; it’s a holistic approach that focuses on regenerating the land, conserving resources, and creating a self-sufficient ecosystem.
Whether you have a small backyard, a rooftop garden, or a larger plot of land, permaculture can help you grow fresh, organic food year-round while reducing reliance on grocery stores.
Let’s explore the principles of permaculture, how to start your own food forest, and the practical steps to achieving a self-sustaining lifestyle.
What is Permaculture?
Permaculture, a term coined by Bill Mollison and David Holmgren in the 1970s, combines “permanent” and “agriculture.” It’s a design philosophy that mimics natural ecosystems to create sustainable food production systems.
Unlike conventional farming, which depletes soil and requires synthetic fertilizers, permaculture focuses on:
- Building healthy soil through composting and natural mulching
- Maximizing biodiversity with companion planting and food forests
- Conserving water through rainwater harvesting and swales
- Using natural pest control instead of harmful chemicals
By applying these principles, anyone can create a self-sustaining garden that thrives with minimal effort over time.
How to Start Your Own Permaculture Garden
1. Design Your Space Thoughtfully
Before planting, observe your land and understand factors like sunlight, wind patterns, and soil quality. Permaculture encourages a zoned approach:
- Zone 1: Close to the house for high-maintenance plants (herbs, salad greens).
- Zone 2: Fruit trees, shrubs, and perennials.
- Zone 3: Larger crops like grains, corn, and potatoes.
- Zone 4: Forested areas for foraging and timber.
- Zone 5: A wild, untouched area to support biodiversity.
Even if you live in an urban setting, balcony gardens or community spaces can follow similar principles.
2. Improve Soil Health Naturally
Healthy soil is the foundation of permaculture. Instead of using chemical fertilizers, focus on natural soil regeneration:
- Composting: Convert food scraps and yard waste into nutrient-rich compost.
- Mulching: Cover soil with leaves, straw, or wood chips to retain moisture and prevent erosion.
- Crop rotation: Plant different crops each season to replenish soil nutrients.
Building living soil ensures that plants stay healthy without the need for synthetic inputs.
3. Grow a Diverse Range of Plants
Diversity is key in permaculture. Unlike monoculture farming, which depletes soil, permaculture encourages companion planting:
- Tomatoes and basil: Basil repels pests while enhancing tomato flavor.
- Corn, beans, and squash (Three Sisters Method): Beans enrich the soil with nitrogen, corn provides structure, and squash prevents weeds.
- Marigolds and vegetables: Marigolds deter harmful insects naturally.
By planting a variety of crops together, you create a self-sustaining ecosystem where plants support each other.
4. Water Wisely with Rainwater Harvesting
Instead of relying on municipal water, permaculture emphasizes natural water conservation:
- Install rain barrels to collect and store water for irrigation.
- Use swales (shallow ditches) to slow and direct water flow.
- Plant drought-resistant crops like sweet potatoes and kale in dry climates.
Efficient water management reduces waste and keeps plants thriving year-round.
5. Incorporate Animals for a Balanced Ecosystem
Animals play a crucial role in permaculture by fertilizing the soil, controlling pests, and providing food.
- Chickens help aerate soil while producing eggs.
- Bees pollinate plants and boost crop yields.
- Ducks eat pests like slugs and mosquitoes.
If you have limited space, even a small worm composting system (vermiculture) can enrich your soil naturally.
6. Use No-Dig Gardening for Low-Maintenance Growing
The no-dig method improves soil structure and retains nutrients by avoiding unnecessary tilling. Instead of plowing, simply:
- Layer compost, cardboard, and mulch on top of the soil.
- Plant directly into the compost layer.
- Let earthworms and microbes naturally break down organic matter.
This technique reduces weeds, retains moisture, and requires less manual labor over time.
7. Save Seeds for Future Planting
Seed saving is an essential skill in permaculture. Instead of buying seeds every season, learn to harvest and store seeds from your best plants.
- Tomatoes, peppers, beans, and squash are great for beginner seed savers.
- Store seeds in a cool, dry place for long-term viability.
- Swap seeds with other gardeners to promote biodiversity.
This ensures you always have access to heirloom and organic varieties suited to your climate.
The Benefits of Permaculture Living
✅ Reduced reliance on grocery stores: Grow your own fruits, vegetables, and herbs, cutting down on food costs.
✅ Healthier, chemical-free food: No pesticides or synthetic fertilizers mean cleaner, nutrient-rich produce.
✅ Environmental impact: Permaculture gardens restore ecosystems, prevent soil degradation, and reduce carbon footprints.
✅ Resilience in uncertain times: With rising food prices and supply chain disruptions, self-sufficiency is more important than ever.
Conclusion: Take the First Step Toward Self-Sufficiency
Permaculture isn’t just a gardening method—it’s a lifestyle shift that promotes sustainability, food security, and harmony with nature. Whether you’re starting with a few container plants or a full-scale food forest, the principles of permaculture can help you grow your own food and live more sustainably.
By applying these strategies, you’ll not only reduce your environmental impact but also gain independence from the modern food system.
Ready to get started? Take the first step by observing your space, improving soil health, and planting a small garden. Over time, you’ll build a self-sustaining system that provides fresh, organic food for years to come.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0